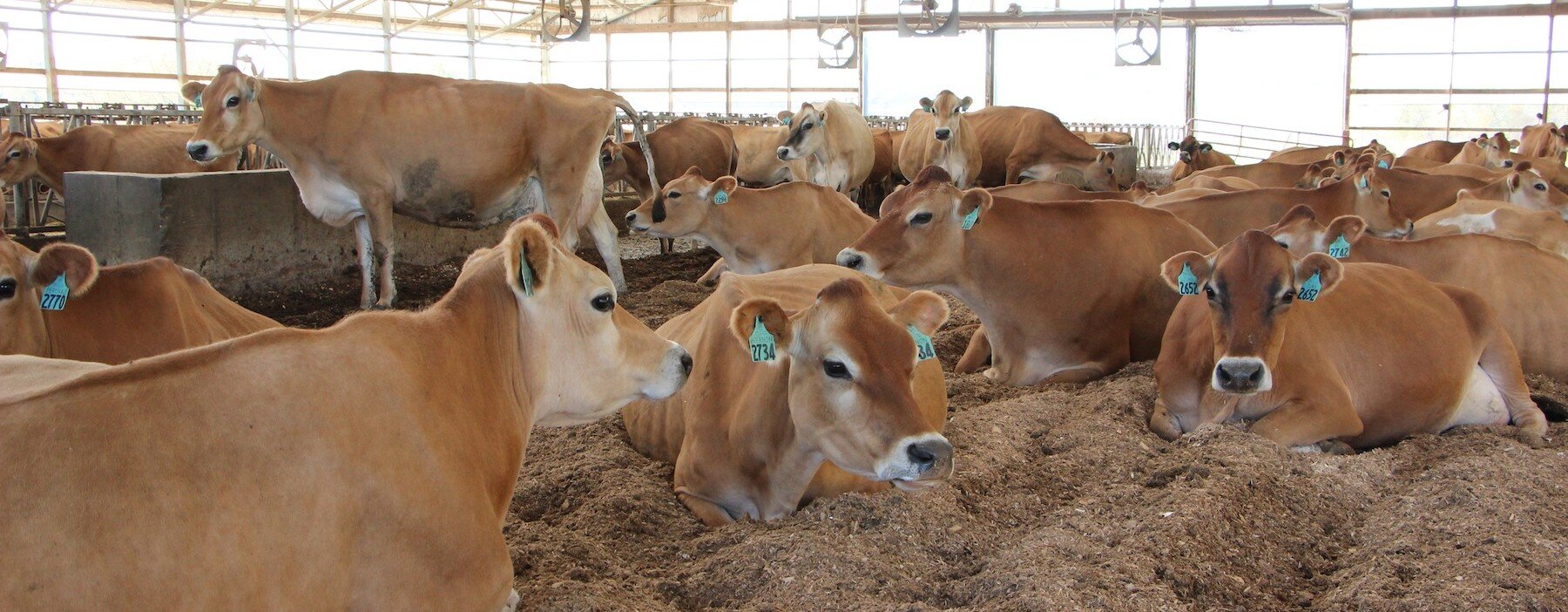
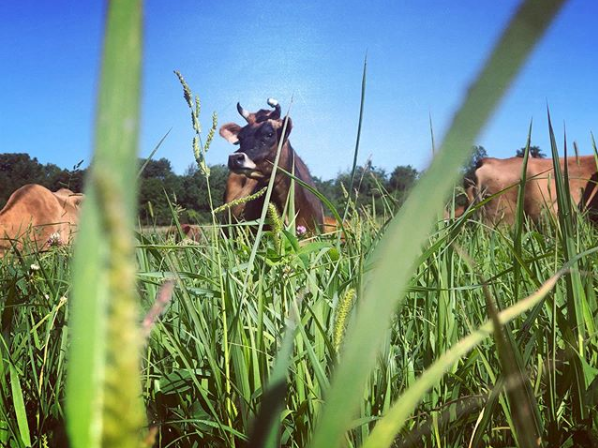
Feeding dairy animals on green sunny pastures is the preferred way to produce raw milk. Paddock rotations that provide a daily cycle of movement to fresh, sunny, green pastures provides an ideal environment for keeping dairy animals healthy, clean, and producing high-quality raw milk. In many cases when dairy farmers transition from an industrial confinement feeding model to a pasture-based feeding system, they are pleased to find that animal health often improves.
Soil fertility and rotational grazing are of prime importance to pasture management. Fertile soil is the main source for minerals taken up by the forage plants which dairy animals graze upon. Soils supplied with calcium and phosphorus fortify milk with these minerals which are needed by people to build strong bones.
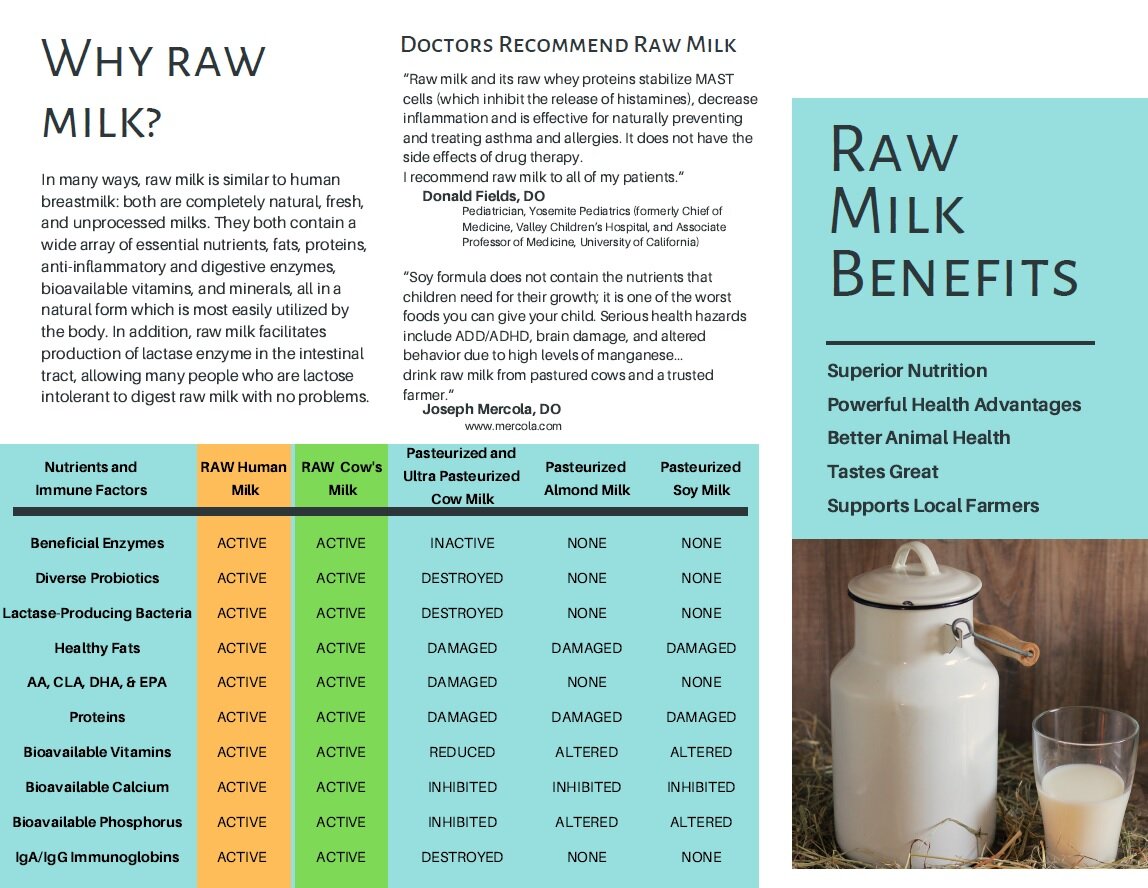
Besides soil being a source for mineral enrichment of milk, a substantial body of scientific literature reports that milk produced by animals on pasture has enhanced nutritional properties compared to milk produced by confinement operations. Milk produced during the grazing season has a more favorable ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids. Pasture raised milk also has higher levels of conjugated linoleic acid and fat-soluble vitamins that are beneficial to human nutrition.
Whether soil fertility is managed or neglected can also influence the health of dairy animals. Sometimes pasture lands are neglected and not managed to optimize soil fertility, forage quality, and health and productivity of grazing animals. For example, an imbalance of the minerals calcium, magnesium, and potassium in soils can put animal health at risk. When soil pH management and liming are neglected weedy plant species may be favored over the more nutritious leguminous forage species preferred by dairy cows.
To produce raw milk of the highest quality, producers should make observations as they walk over the pastures grazed by dairy animals. In weedy pastures where more desirable forage species are failing to thrive, it may be a sign of poor soil fertility or other mismanagement. Soil sampling and testing for soil fertility status can be performed to help diagnose reasons for poor pasture performance. Even on seemingly well performing pastures, regular soil fertility sampling and testing should be done about every three years to monitor soil pH and fertility status.
A new publication Soil Fertility Recommendations for Pastures is now available online from Rutgers University, New Jersey Agriculture Research Station (E364 Soil Fertility Recommendations for Pastures. Heckman, J. https://njaes.rutgers.edu/e364 ). Although this publication was specifically designed for New Jersey much of the information is universal. The main soil fertility guidelines are most applicable to Eastern and Midwestern states. Higher levels of precipitation in the Eastern states cause nutrients to leach and acidify the soil. This increases the need to apply limestone more frequently.
In other regions, soil fertility needs, and testing procedures may be different and based on the local geological and climatic conditions. For instance, soils in the arid Southwest tend to be alkaline and as such the pastures may benefit from acidifying soil amendments. Also, different climatic regions may grow different forage species. To account for regional differences, farmers should consult with local expertise for soil fertility recommendations.
Image from Oregon State University
In summary, producers of fresh unprocessed milk are encouraged to make the best use of pastures as a major feed source during the grazing season. When the soil fertility conditions are optimized for the health and productivity of dairy animals, farmers will be able to provide customers with nutritious dairy products of the highest quality.