The Raw Milk Institute (RAWMI) is on a mission to improve the safety and quality of raw milk and raw milk products through farmer training, rigorous raw milk standards, raw milk research, and improving consumer education.
In 2020, RAWMI was awarded a 2nd grant from the Regenerative Agriculture Foundation (RAF) to further our work. RAWMI matches an economic benefit of stewardship of pastures and soils to high value raw dairy products for consumers. Safe raw milk from pastured cows can sustain the farm financially while the grazing improves the soils.
With the 2nd grant from RAF, RAWMI was able to accomplish much towards the overall goal of universal access to safe raw milk. With the unique challenges of 2020, RAWMI was able to adapt to the changing conditions and successfully develop new models for training and outreach.
Over the last year, RAWMI:
Gave 14 raw milk training presentations (via Zoom)
Trained over 500 farmers, legislators, university professors, and consumers on raw milk benefits and risk management (via Zoom)
Prepared and presented an intensive 4.5 hour training course on Raw Milk Risk Management, for the Ohio Ecological Food and Farming Association (OEFFA)
LISTED six new farms, who went through the process of developing an individualized Risk Assessment and Management Plan (RAMP) for managing the health and hygiene of their unique farms
Provided one-on-one mentoring in the production of low-risk raw milk to over 25 additional farms in California, Michigan, Virginia, Michigan, Panama, Argentina, South Dakota, Hawaii, Montana, Washington, Tennessee, North Dakota, Oregon, Connecticut, and British Columbia
Hosted quarterly meetings for LISTED farmers, which allow the farmers to stay up-to-date on the latest lessons learned for safe raw milk
Amassed hundreds of raw milk test data from RAWMI LISTED farms
Attended and sponsored International Milk Genomics Consortium Conference (via Zoom)
Collaborated with raw milk researchers in better understanding trends in raw milk-related outbreaks and illnesses
Worked towards legalization of interstate raw butter and increased legal access to raw milk in Oregon and South Carolina
Published 20 content pieces on the RAWMI website
Provided on-farm lab grants to 4 farms
Provided scholarships for OEFFA training to 10 farmers
Raw Milk Training
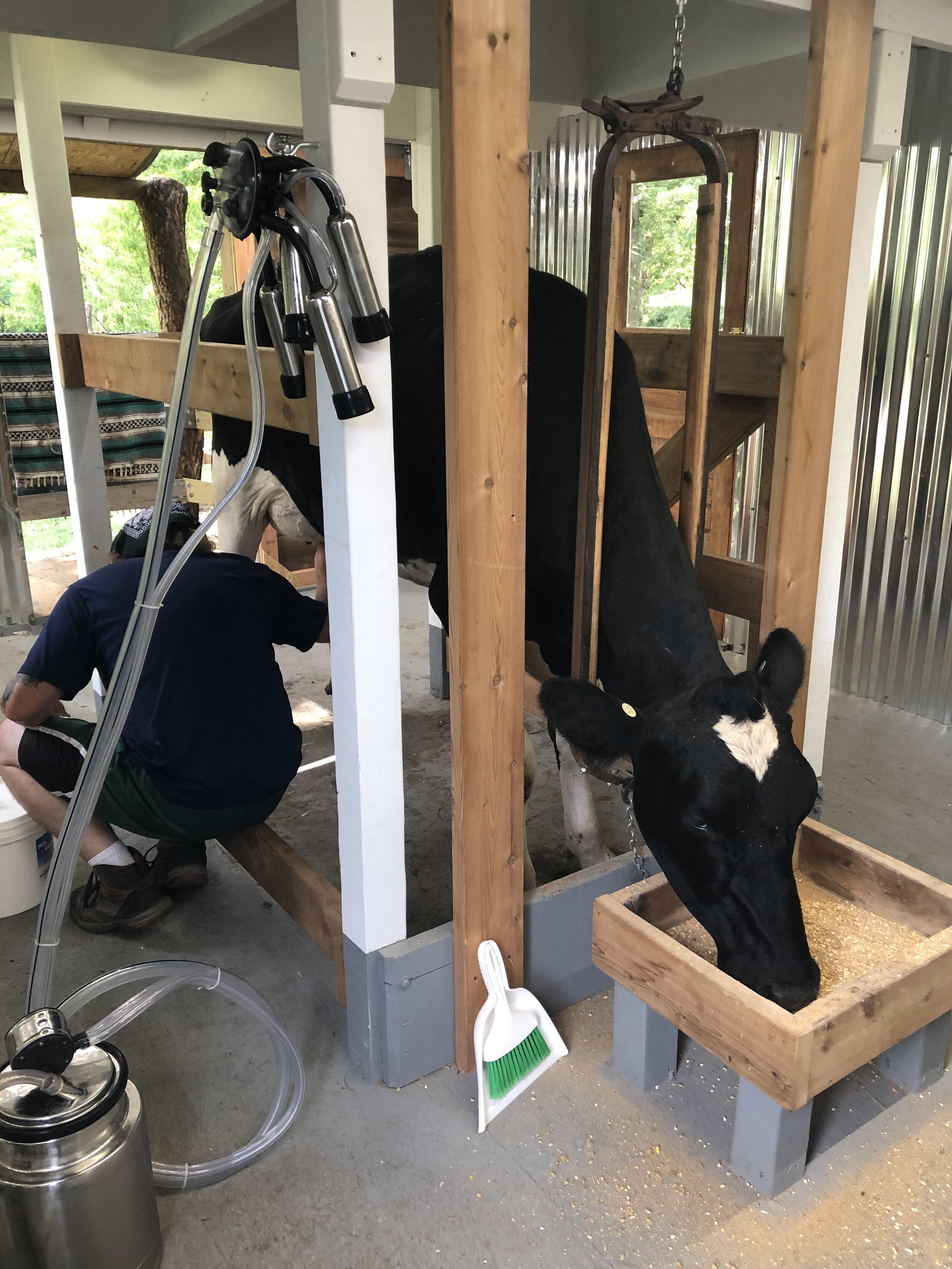
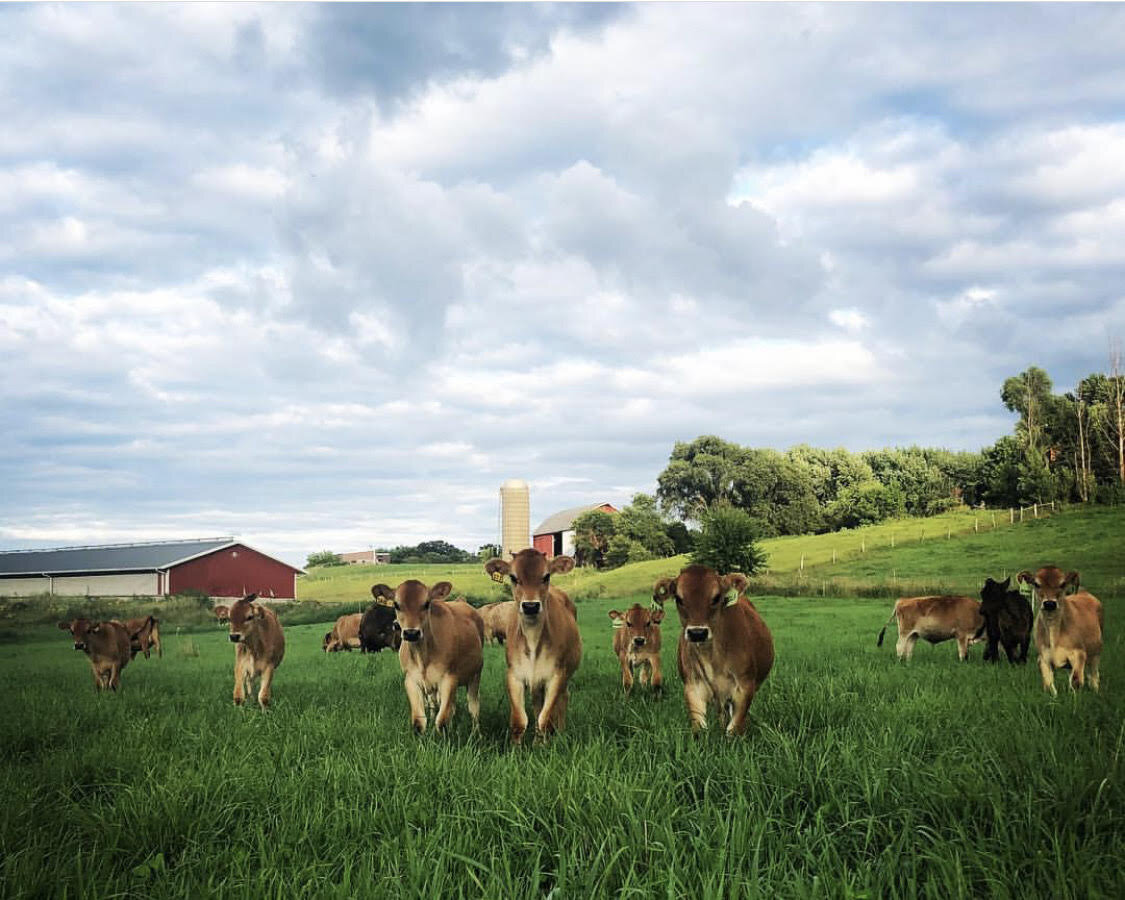
RAWMI taught about raw milk health benefits and safety throughout the United States. Whenever RAWMI teaches about raw milk risk management, soil and conditions management are emphasized as key elements in creating healthy, sustainable farms.
Dairy animals grazing on pastures provide a critical link to the soil biome and restorative farm practices. Pasture-based dairy farms produce healthy soils that are rehabilitated and renewed through the cycle of returning organic carbon to the soil in the form of plants biomass and manure. The resulting food that is harvested by either the animals or the farmer is rich in nutritional elements needed for human health.
Via Zoom, raw milk training was presented to over 500 farmers, legislators, university professors, and consumers in association with the following:
Ohio Ecological Food and Farming Association
Take Back Your Health Symposium
Village Fitness and Physical Therapy
Andrew Columbini (Los Angeles blogger)
Pennsylvania Grazer’s Convention
Mid-Atlantic Agriculture Convention
Attendees at RAWMI’s training classes provided feedback such as the following.
“I so enjoyed the RAWMI training yesterday. It was quite energizing to be surrounded virtually with like-minded individuals wanting to produce exceptionally high quality raw milk. For me, the combination of technical information and anecdotes is very effective for explaining why the RAWMI methods are important and how they solve a raw milk producer challenges. I came away with practical solutions to increase the quality/value of our milk and farm. Thank you."
“I left the Zoom meeting with a very clear understanding of what we are doing right and where we need to make changes. Beyond that, though, I left inspired to pursue excellence and cast a clear vision to everyone who is joining me in this endeavor.”
“The information was also rich and informative. I learned a ton and the systematic way you presented it was easy to follow and comprehensive.”
“I cannot wait to move forward with you in becoming RAWMI Listed. We will be making some changes as we form our RAMP plan. We have already adjusted our milk chilling and have seen an improvement in flavor and longevity.”
“Thank you for all you do. I have no doubt history will look back at the RAWMI as having played a crucial role in reforming raw milk production, health, and nutrition.”
“Excellent presentation that every single person who dairies for themselves and their family should take and learn from. Thank you very much.”
“This has been excellent! ONLINE was so helpful as it’s hard to travel and be away.”
Farmer Mentoring
RAWMI worked with individual farmers across the United States, Canada, and South America. RAWMI provided one-on-one mentoring and troubleshooting support for low-risk raw milk production, including helping farmers optimize their raw milk production, overcome problems in their milk systems and testing, and learn more about successful business practices. This mentorship benefited farmers in:
California
Michigan
Virginia
Wyoming
Panama
Argentina
South Dakota
Hawaii
Montana
Washington
Tennessee
North Dakota
Oregon
Connecticut
British Columbia
RAWMI LISTED Farms
RAWMI LISTED farmers are dedicated to producing clean, safe raw milk. The RAWMI listing process involves the development of individualized Risk Assessment and Management Plans (RAMPs) for managing the health and hygiene of each unique farm. RAWMI LISTED farms submit test data monthly to show that they are in compliance with RAWMI Common Standards, which target a rolling three-month average of <5,000 standard plate count (SPC) and <10 coliforms per ml of raw milk.
In the last year, RAWMI LISTED five more farms, in Virginia, Michigan, Kansas, and Wisconsin. To-date, RAWMI has LISTED 25 farms, and there are currently 20 active LISTED farms in the United States and Canada
RAWMI provided continuing support to all LISTED farmers to enable sustained excellence in low-risk raw milk. This included quarterly meetings for LISTED farmers, which allow the farmers to stay up-to-date on the latest lessons learned for safe raw milk, exchange ideas for improvements, and collaborate with the RAWMI Board of directors.
RAWMI also sponsored general raw milk educational outreach and advertising through social media. This outreach specifically targeted regions across the United States where RAWMI LISTED dairies are located, to connect consumers to LISTED farmers.
Raw Milk Research and Science
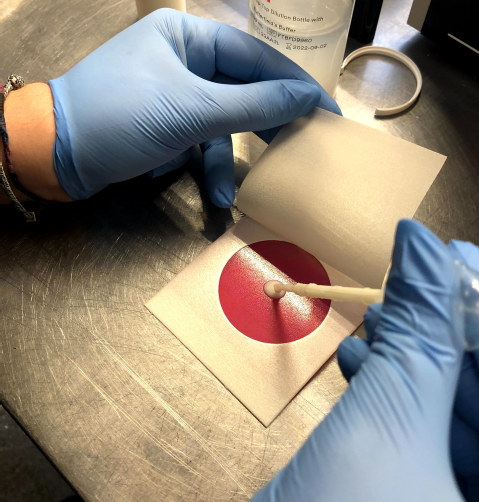
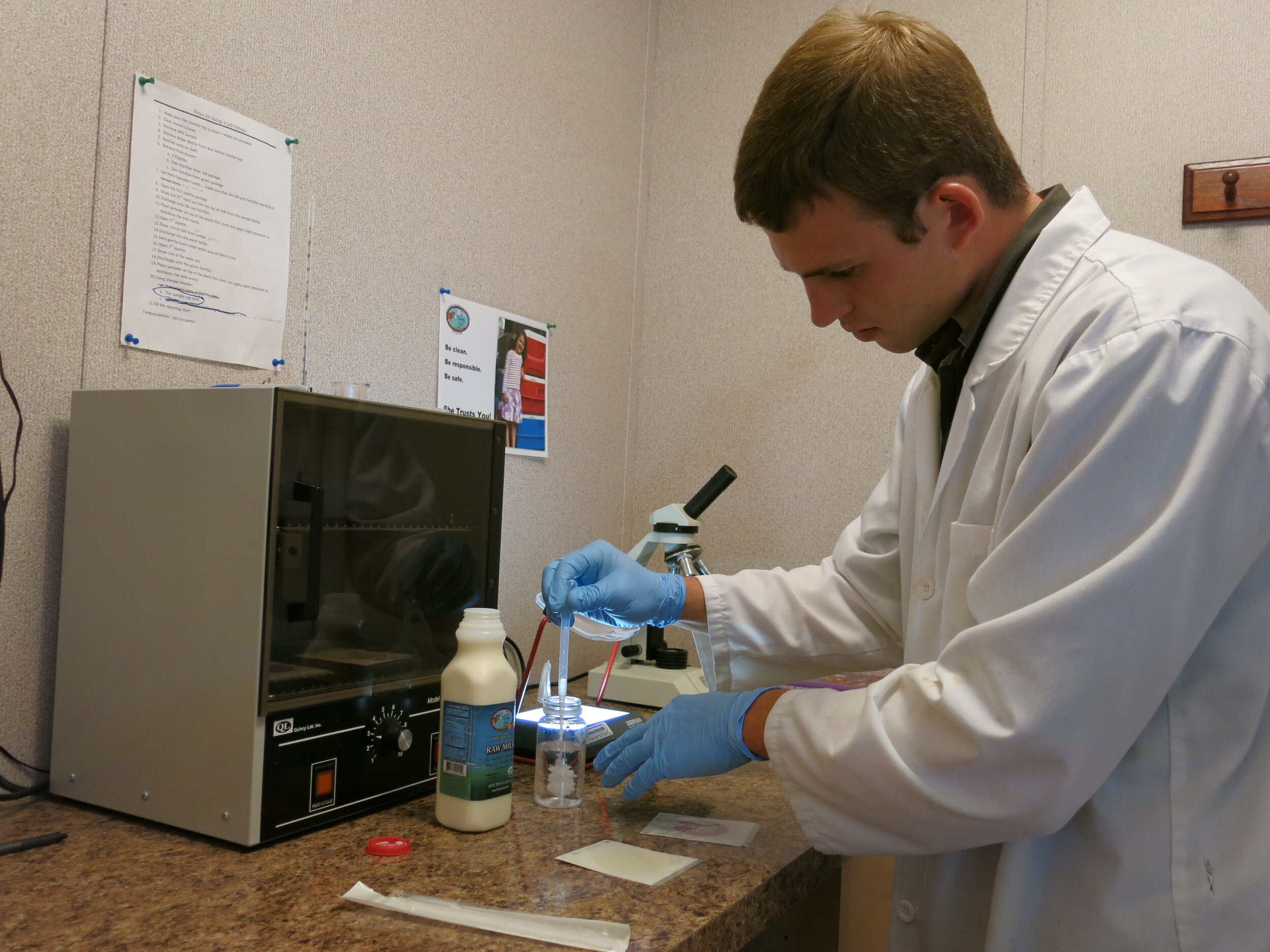
RAWMI’s mission includes supporting raw milk research and science. RAWMI LISTED farmers test their milk at least monthly for coliforms and Standard Plate Count (SPC). These tests provide a way to measure the amount of bacteria present in the milk, as well as providing a measure of the overall hygiene and cleanliness of the milk. Monthly testing serves as a useful confirmation step for ensuring that raw milk is being produced in a way that discourages pathogen growth and is therefore low-risk.
Test data from LISTED farms is submitted to RAWMI monthly. RAWMI amassed hundreds of test data from RAWMI LISTED farms over the last year. This data can be used for raw milk research.
RAWMI was a sponsor of the 17th International Milk Genomics Consortium (IMGC) and attended the virtual IMGC conference. As part of that conference, RAWMI is now engaged with international research and relationships with PhD researchers across the world. The IMGC provides access to the most leading-edge studies on milk genomics.
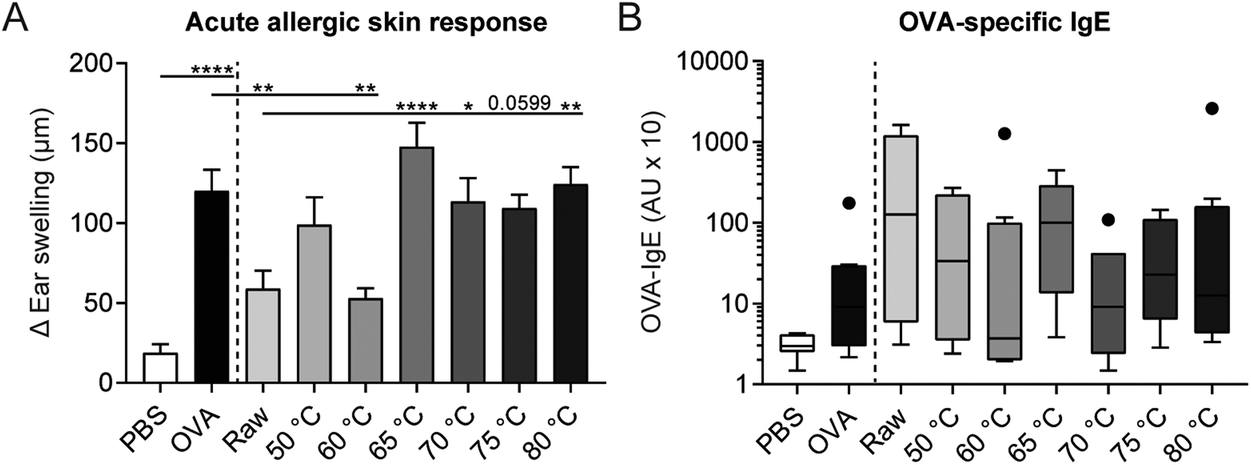
One of the studies presented at the conference this year was related to the loss of allergy-protective capacity of raw milk due to heating. This study “tested the various heat-treated milk samples for their native protein profile and their allergy-protective capacity... the allergy-protective effect of raw cow's milk is lost after heating milk for 30 min at 65 °C [149 °F] or higher. This loss of protection coincided with a reduction in native immunologically active whey proteins.” The whey protein in raw milk provides protection from allergies, asthma, and inflammation. When heated above 149 °F, these properties are dramatically reduced or eliminated. This finding is an important confirmation of the unique beneficial properties of whole, unprocessed raw milk.
Raw Dairy Legalization and Support
RAWMI collaborated with the Farm-to-Consumer Legal Defense Fund (FTCLDF) towards the legalization of raw butter. Raw butter is an exceptionally nutritious food. For instance, the enzyme alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is found in the butter fat membrane that covers fat globules. ALP decreases inflammation in the body; it is associated with good health and less chronic illness, such as cardiovascular disease and Type-2 diabetes. Raw milk has 4% butter fat, but raw butter contains 86% fat and thus it is very high in alkaline phosphatase. ALP enzyme is destroyed by pasteurization. The case for legalization of raw butter is currently going through the court system.
RAWMI is also working towards legalization of raw milk in specific states. RAWMI provided testimony to lawmakers in Oregon and South Carolina. Furthermore, RAWMI worked with the Organic Farmers Association and the National Farmers Union to create national policies for raw milk.
Raw Dairy Educational Outreach
RAWMI created numerous educational materials and articles for raw milk consumers and the general public. 20 articles were published to the RAWMI website and social media, with a wide array of topics including:
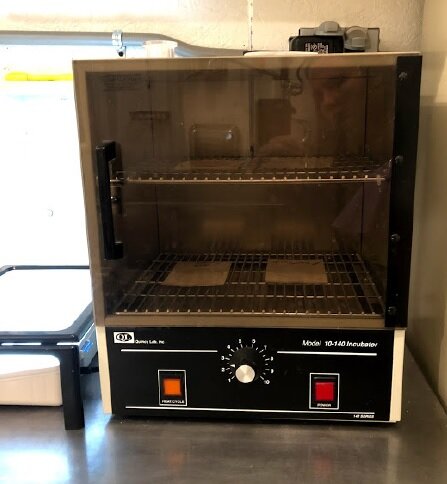
On-Farm Lab Sponsorships
RAWMI sponsored four farms in building on-farm labs for raw milk bacterial testing. On-farm lab testing is a powerful tool for raw milk farmers. It allows for frequent testing, so farmers can better identify issues before they turn into big problems, and it also helps immeasurably with troubleshooting when needed. On-farm labs require an initial investment of $800-$1,000, but once the lab is in-place the cost per test is only $1-$3. With RAWMI’s sponsorship, four farms were able to build their own on-farm labs for testing coliforms and Standard Plate Count.